The effect of RE substitution in layered REO0.5F0.5BiS2: chemical pressure, local disorder and superconductivity
Abstract
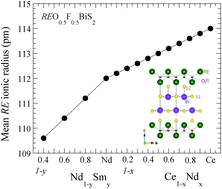
We have studied the effect of RE substitution on the structure and the local atomic disorder in REO0.5F0.5BiS2 (RE = rare-earth) to understand their correlation with the bulk superconductivity in these materials. The mean RE size, affecting the chemical pressure, has been varied in two series namely Ce1−xNdxO0.5F0.5BiS2 and Nd1−ySmyO0.5F0.5BiS2. The lattice parameters evolve anomalously, showing an anisotropic shrinkage (elongation) of the c-axis (a-axis) to an isotropic expansion of the lattice with increasing mean RE size. The Bi L3-edge extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) measurements are performed to investigate local displacements in the BiS2 lattice, revealing a large disorder and a sharp boundary between the Ce-containing and Sm-containing series with a distinct local structure. The results suggest that the bulk superconductivity in REO0.5F0.5BiS2 is correlated with anomalous atomic displacements in the Bi–S1 network, likely to be a combined effect of active Bi 6s electronic states and a possible Jahn–Teller-like instability of the Bi 6px/6py electrons.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...