Temperature dependent structural variations of OH−(H2O)n, n = 4–7: effects on vibrational and photoelectron spectra†
Abstract
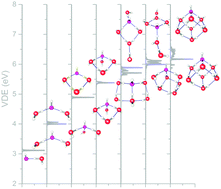
In this work, we identified a large number of structurally distinct isomers of midsized deprotonated water clusters, OH−(H2O)n=4–7, using first-principles methods. The temperature dependence of the structural variation in the solvation shell of OH− for these clusters was examined under the harmonic superposition approximation. We simulated the vibrational and photoelectron spectra based on these thermodynamic calculations. We found that the isomers with 3-coordinated hydroxide dominate the population in these midsized clusters. Furthermore, an increase in temperature causes a topological change from compact isomers with many intermolecular hydrogen bonds to open isomers with fewer but more directional intermolecular hydrogen bonds. We showed that this evolution in structure can be observed through the change in the vibrational spectra at 3200–3400 cm−1. In addition, the increase in directional hydrogen bonded isomers, which have outer hydration shell with OH bonds pointing to the hydroxide, causes the vertical detachment energy to increase at higher temperatures. Lastly, we also performed studies to understand the variation in the aforementioned spectral quantities with the variation in the coordination number of the hydroxide.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...