O2 and H2O2 transformation steps for the oxygen reduction reaction catalyzed by graphitic nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes in acidic electrolyte from first principles calculations†
Abstract
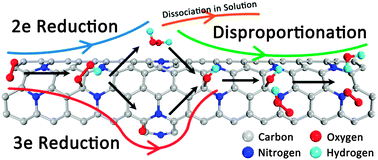
It is highly challenging but extremely desirable to develop carbon catalysts with high oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activity and stability in acidic medium for commercial application. In this paper, based on density functional theory (DFT) calculations with long range interaction correction and solvation effects, the elementary transformations of all the probable intermediates in the ORR and the hydrogen peroxide reduction reaction (HPRR) over graphitic nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes (NCNTs) in acidic medium were evaluated, and it was found that all the rate determining steps are related to the bonding hydroxyl group because of the strong interaction between the hydroxyl group and carbon. Thus, it is hard for the direct four-electron ORR and the two-electron HPRR to proceed. Together with hydrogen peroxide disproportionation (HPD), a mixed mechanism for the ORR in acidic electrolyte was proposed, where the two-electron and three-electron ORRs and HPD dominate the electrode reaction. The experimental result for the ORR catalyzed by NCNTs in acidic electrolyte also well illustrated the rationality of the theoretical calculations. This study not only gives new insights into the effect of graphitic nitrogen doping on the ORR catalyzed by carbon, but also provides a guide to design carbon catalysts with high ORR activity in acidic electrolyte.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...