XPS of guanidinium ionic liquids: a comparison of charge distribution in nitrogenous cations†
Abstract
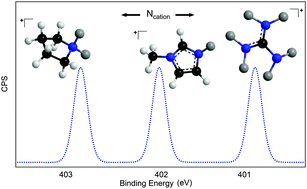
Herein, we investigate the first X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) data for a range of functionalised guanidinium based systems that are commonly employed in the dissolution of biomolecules. We define a peak fitting model which allows the direct comparison to more common cation sets including dialkyl-imidazolium, pyrrolidinium, and quaternary ammonium based systems. The measured binding energies (BEs) of the N 1s and C 1s components are presented and notable variations discussed. These data show a large difference between measured binding energies for the Ncation 1s when compared to other families of ionic liquids. These results suggest a weaker anion/cation interaction thus the anion is more able to interact with a solid matrix, i.e. keratin, silk, chitin, collagen, cellulose, and become more active in dissolution.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...