Electric field control of proton-transfer molecular switching: molecular dynamics study on salicylidene aniline
Abstract
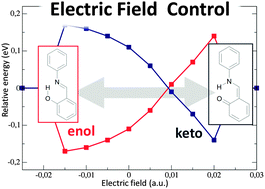
In this letter, we propose a novel, ultrafast, efficient molecular switch whose switching mechanism involves the electric field-driven intramolecular proton transfer. By means of ab initio quantum chemical calculations and on-the-fly dynamics simulations, we examine the switching performance of an isolated salicylidene aniline molecule and analyze the perspectives of its possible use as an electric field-controlled molecular electronics unit.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...