Enhanced field emission from in situ synthesized 2D copper sulfide nanoflakes at low temperature by using a novel controllable solvothermal preferred edge growth route†
Abstract
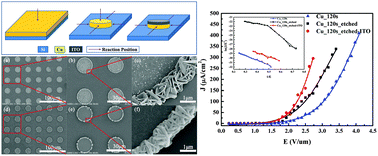
A facile one-pot solvothermal route using the reaction of sputtered copper film and sulfur powder in ethanol solution at a low temperature of 90 °C for 12 hours has been implemented to in situ synthesize 2D hexagonal copper sulfide (CuS) nanoflakes. Their field electron emission (FE) characteristics were investigated and were found to have a close relationship with the copper film’s thickness. The lowest turn on electric field (Eon) was 2.05 V μm−1 and the largest field enhancement factor (β) was 7261 when the copper film's thickness was 160 nm. Furthermore, through a preferred edge growth route, patterned CuS nanoflakes were synthesized with the combined effect from a copper film seed layer and a passivation layer to further improve FE properties with an Eon of 1.65 V μm−1 and a β of 8351. The mechanism of the patterned CuS nanoflake preferred edge growth is reported and discussed for the first time.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...