Reaction-diffusion degradation model for delayed erosion of cross-linked polyanhydride biomaterials
Abstract
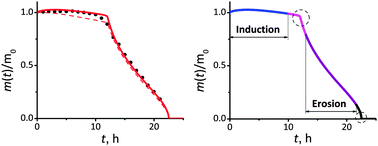
We develop a theoretical model to explain the long induction interval of water intake that precedes the onset of erosion due to degradation caused by hydrolysis in the recently synthesized and studied cross-linked polyanhydrides. Various kinetic mechanisms are incorporated in the model in an attempt to explain the experimental data for the mass loss profile. Our key finding is that the observed long induction interval is attributable to the nonlinear dependence of the degradation rate constants on the local water concentration, which essentially amounts to the breakdown of the standard rate-equation approach, potential causes for which are then discussed. Our theoretical results offer physical insights into which microscopic studies will be required to supplement the presently available macroscopic mass-loss data in order to fully understand the origin of the observed behavior.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...