Nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticles derived from acrylonitrile plasma for electrochemical oxygen reduction†
Abstract
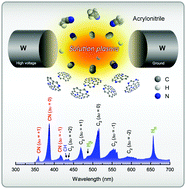
Nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticles were synthesized via a solution plasma process, with acrylonitrile as a single-source precursor, followed by a post-thermal annealing process. The nitrogen-bonding states can be tuned by varying the annealing temperature. The best electrocatalytic activity for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in terms of both onset potential and limiting current density can be achieved for the catalyst annealed at an optimal temperature of 800 °C because of the high content of graphitic-N catalytic sites and a large specific surface area.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...