Influence of stearic acid coating of the NaCl surface on the reactivity with NO2 under humidity†
Abstract
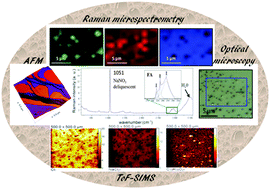
In the atmosphere, sea salt aerosols, containing mainly NaCl, can accumulate fatty acids and undergo heterogeneous chemistry with atmospheric nitrogen oxides. The effect of stearic acid (SA) coating on the reactivity of the NaCl(100) surface with NO2 under humidity was studied by atomic force microscopy (AFM), Raman mapping and time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (ToF-SIMS) to highlight processes occurring on NaCl surfaces. The vapor-deposition of SA on the NaCl surface generates heterogeneous coating with discontinuous monolayer islands. The SA molecules with all-trans conformation stick to the NaCl surface through –CO2H groups and are organized in parallel between them and nearly perpendicularly to the surface. The SA coating does not prevent the NaNO3 particle formation when the sample is exposed to NO2 under low humidity conditions. The initial abilities of the NaCl surface coated with SA to pick up NO2 from the gas phase are correlated with the fraction of bare NaCl area evidencing the spatially heterogeneous reactivity of the surface. The role of H2O in the NO2 uptake and the catalytic conversion of NaCl to NaNO3 is shown. Under humidity (RH = 50%), the H2O uptake by NaNO3 particles on the coated-NaCl surface is significantly more important than that adsorbed under analogous conditions without the presence of NaNO3 particles. This unusual water absorption initiates transitions (i) from solid NaNO3 particles to NaNO3 aqueous solution and (ii) from the SA monolayer with well-ordered all trans alkyl chains to the SA gel with completely disordered conformation. This mixed SA/NaNO3 layer on the particle surface may have significant consequences on the hygroscopic properties and reactivity of the sea salt aerosols in the atmosphere.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...