Adsorbate-driven morphological changes on Cu(111) nano-pits
Abstract
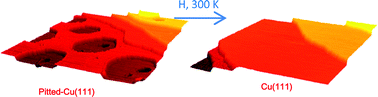
Adsorbate-driven morphological changes of pitted-Cu(111) surfaces have been investigated following the adsorption and desorption of CO and H. The morphology of the pitted-Cu(111) surfaces, prepared by Ar+ sputtering, exposed a few atomic layers deep nested hexagonal pits of diameters from 8 to 38 nm with steep step bundles. The roughness of pitted-Cu(111) surfaces can be healed by heating to 450–500 K in vacuum. Adsorption of CO on the pitted-Cu(111) surface leads to two infrared peaks at 2089–2090 and 2101–2105 cm−1 for CO adsorbed on under-coordinated sites in addition to the peak at 2071 cm−1 for CO adsorbed on atop sites of the close-packed Cu(111) surface. CO adsorbed on under-coordinated sites is thermally more stable than that of atop Cu(111) sites. Annealing of the CO-covered surface from 100 to 300 K leads to minor changes of the surface morphology. In contrast, annealing of a H covered surface to 300 K creates a smooth Cu(111) surface as deduced from infrared data of adsorbed CO and scanning tunnelling microscopy (STM) imaging. The observation of significant adsorbate-driven morphological changes with H is attributed to its stronger modification of the Cu(111) surface by the formation of a sub-surface hydride with a hexagonal structure, which relaxes into the healed Cu(111) surface upon hydrogen desorption. These morphological changes occur ∼150 K below the temperature required for healing of the pitted-Cu(111) surface by annealing in vacuum. In contrast, the adsorption of CO, which only interacts with the top-most Cu layer and desorbs by 200 K, does not significantly change the morphology of the pitted-Cu(111) surface.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...