The effect of the functionalization and molecular weight of cationic dextran polyelectrolytes on their electrochemical behavior at the water/1,2-dichloroethane interface
Abstract
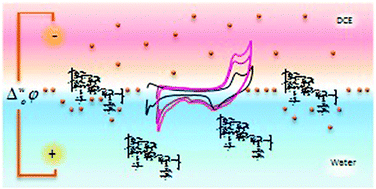
The electrochemical behaviour of several cationic dextran polyelectrolytes, aminodextran (AD), cationic dextran (CD) and diethylaminoethyl dextran (DEAE-D), at the polarized water/1,2-dichloroethane interface was studied. An investigation into the influence of the scan rate, concentration, pH, the nature and the concentration of the anion present in the organic electrolyte and the effect of the polymer molecular weight is presented. Different responses were obtained and explained considering the structural difference between these species, mainly the position of the positive charge in the macromolecule. The AD polymer is not transferred to the organic phase, regardless of molecular weight, while CD and DEAE-D are transferred from the aqueous to the organic phase at E = 0.650 V, independent of the polymer concentration and of the molecular weight. The shape of the voltammograms corresponding to DEAE-D transfer as well as the magnitude of the peak currents and the peak potential values were all dependent on the pH of the aqueous phase solution and on the nature and concentration of the anion present in the organic electrolyte. Based on this dependence, we postulated a mixed mechanism, which involves the transfer of dissolved and adsorbed DEAE-D molecules.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...