Axis symmetry of silicon molten zone interface shape under a mirror-shifting-type infrared convergent-heating floating-zone method
Abstract
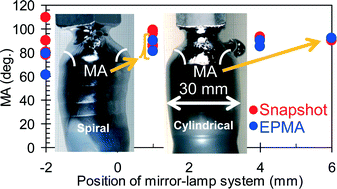
The shape of the silicon crystal, whether spiral or cylindrical, was grown using the infrared convergent-heating floating-zone method, and the stability of the molten zone depended on the position of the mirror-lamp (M-L) system with respect to the grown crystal and molten zone. Through experiment, we studied the changes in the molten zone shape: the melt/feed, melt/gas, and melt/crystal interface shapes of the silicon molten zone under different positions of the M-L system. Although conventional parameters such as convexities (h/r) of the interface toward the melt were found to be independent of the position of the M-L system, the asymmetry of the zone length, L, was found to be inversely proportional to the distance of the M-L system from the center of the molten zone. A spiral crystal would be grown in this case. We introduce some parameters such as growth interface angle (δ), triple point angle (TPA), meniscus angle (MA), and altitude of the interface curvature (aC) to characterize the axis symmetry of the melt/gas and melt/crystal interfaces. The variations in TPA, MA, and aC were significantly reduced when the M-L system was shifted to a distant position from the center of the molten zone. On the other hand, the variations in δ were independent of the position of the M-L system. Thus, a symmetric molten zone was observed when the M-L system was at a distant rather than a close position. These behaviors were validated through observations of the molten zone stability and the crystal shape.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...