Electrochemical and chemical insertion/deinsertion of magnesium in spinel-type MgMn2O4 and lambda-MnO2 for both aqueous and non-aqueous magnesium-ion batteries†
Abstract
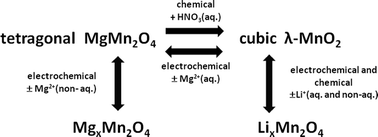
By using both chemical and electrochemical methods, magnesium has been reversibly removed from MgMn2O4 (s.g. I41/amd) with appropiate texture to form single-phase and nanocrystalline λ-MnO2 (s.g. Fd![[3 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0033_0304.gif) m). Cubic λ-MnO2 is not stable after annealing in both air and Ar atmospheres. The oxidation of Mn(III) to Mn(IV) eliminates the tetragonal distortion of the spinel-type lattice, but λ-MnO2 is more effectively obtained when powdered MgMn2O4 has a large specific surface area and a small particle size. In an aqueous solution of a magnesium salt, λ-MnO2 is formed by galvanostatic charge of MgMn2O4 and continuous Ar-flowing for removing oxygen from the solution. Starting from λ-MnO2, the tetragonal structure of MgMn2O4 and the cubic structure of LiMn2O4 are generated by electrochemical cycling in aqueous solutions containing salts of magnesium and lithium, respectively. In an aqueous solution cell, this material exhibits a reversible capacity of about 150 mA h g−1 and can be used in magnesium-ion batteries demonstrating it to be competitive against their lithium counterparts. In the absence of metallic Mg, the use of carbonate-based solvents can be a good choice for veritable non-aqueous magnesium-ion batteries, for example using positive electrode materials like MgMn2O4 (magnesium-ion source) and negative electrode materials like V2O5. In non-aqueous solvents (ethylene carbonate–diethyl carbonate mixture), the cubic phase λ-MnO2 is not formed, the tetragonal structure of MgxMn2O4 is preserved and its lattice cell is contracted.
m). Cubic λ-MnO2 is not stable after annealing in both air and Ar atmospheres. The oxidation of Mn(III) to Mn(IV) eliminates the tetragonal distortion of the spinel-type lattice, but λ-MnO2 is more effectively obtained when powdered MgMn2O4 has a large specific surface area and a small particle size. In an aqueous solution of a magnesium salt, λ-MnO2 is formed by galvanostatic charge of MgMn2O4 and continuous Ar-flowing for removing oxygen from the solution. Starting from λ-MnO2, the tetragonal structure of MgMn2O4 and the cubic structure of LiMn2O4 are generated by electrochemical cycling in aqueous solutions containing salts of magnesium and lithium, respectively. In an aqueous solution cell, this material exhibits a reversible capacity of about 150 mA h g−1 and can be used in magnesium-ion batteries demonstrating it to be competitive against their lithium counterparts. In the absence of metallic Mg, the use of carbonate-based solvents can be a good choice for veritable non-aqueous magnesium-ion batteries, for example using positive electrode materials like MgMn2O4 (magnesium-ion source) and negative electrode materials like V2O5. In non-aqueous solvents (ethylene carbonate–diethyl carbonate mixture), the cubic phase λ-MnO2 is not formed, the tetragonal structure of MgxMn2O4 is preserved and its lattice cell is contracted.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...