Co-crystallisation of cytosine with 1,10-phenanthroline: computational screening and experimental realisation†
Abstract
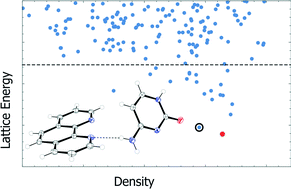
Attempts to co-crystallise the nucleobases adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine with 1,10-phenanthroline by ball milling and solvent evaporation methods are described. A 1 : 1 co-crystal of cytosine and 1,10-phenanthroline can be obtained by grinding or by solvent evaporation. The structure contains two crystallographically independent cytosine and two independent 1,10-phenanthroline molecules (Z′ = 2). The cytosine molecules form two similar but crystallographically independent hydrogen-bonded chains, while the 1,10-phenanthroline molecules are arranged in π-stacks. Between the chains of cytosine and the π-stacks exist N–H⋯N and C–H⋯N interactions. Crystal structure prediction (CSP) calculations were applied to all four systems to assess their potential for co-crystallisation as well as the likely structures and intermolecular interactions that could result from co-crystallisation. Calculations on the cytosine system demonstrate that co-crystallisation results in a lower energy than the crystalline forms of the two starting materials, in line with the co-crystal formation observed. For the systems which did not form a co-crystal, CSP was used to explore potential packing arrangements, but found none which were lower in energy than that of the pure crystalline forms. In these cases there is significant disruption to the nucleobase hydrogen bonding between the pure compound and the hypothetical co-crystal. For pure adenine and guanine, the hydrogen-bonded ribbons form sheets which must be broken, whereas for thymine, the lack of hydrogen bond donors does not allow the hydrogen bonding present for pure thymine to be maintained while forming thymine-1,10-phenanthroline hydrogen bonds.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...