Surface-dependent magnetic behavior of α-Fe2O3 quasi-cubes induced by Mg2+ ions†
Abstract
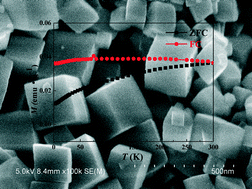
Uniform α-Fe2O3 quasi-cubes with high-index facets exposed were synthesized in a controlled manner through a simple hydrothermal method using Mg2+ ions as structure-directing agents. The as-prepared α-Fe2O3 quasi-cubes are bound by (012), (10−2), and (1−12) facets with an edge length of about 200 nm and a dihedral angle of 86°. In the reaction system, the Mg2+ ions would undertake the role of structure and surface director, adsorb to the α-Fe2O3 high energy surface and induce the α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles to grow into quasi-cubic nanocrystals bound by high-index facets. Magnetic measurements testify that the quasi-cubes display surface-dependent magnetic behavior. The α-Fe2O3 quasi-cubes have a splitting between the FC curve and the ZFC curve from the highest experimental temperature to the lowest temperature and no Morin transformation occurs, indicating that they would be under defect ferromagnetic control both at room temperature and low temperature.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...