Novel ZnO–ZnS nanowire arrays with heterostructures and enhanced photocatalytic properties†
Abstract
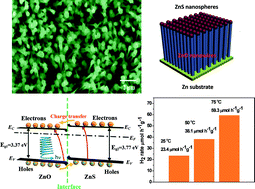
Well-aligned ZnO–ZnS heterojunction nanowire arrays have been synthesized via a novel wet chemical route in which ammonium persulfate was used as an oxidant to oxidize zinc foil directly followed by a sulfidization process to substitute oxygen with sulfur in the alkali solution. The structure and photocatalytic properties of ZnO–ZnS were analysed in comparison with those of ZnO nanowires. The formation mechanism of ZnO–ZnS heterojunction NW arrays arises from a combination of two different processes, namely a typical dissolution–crystallization process and a substitution reaction. Room temperature photoluminescence measurements indicate that ZnO–ZnS heterojunction NW arrays have an emission peak centered at 385 nm, and the PL intensity of the ZnO–ZnS heterojunction is lower than that of the ZnO NW arrays. The morphology and structure of the heterostructural products have been characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Due to the formation of heterostructures and a new transfer pathway of electrons from ZnS to ZnO, the composites show significantly improved photocatalytic activities than that of pure ZnO NW arrays. This study offers a novel way of fabricating semiconductor composites for high-efficiency photocatalysis applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...