Continuous synthesis of dispersant-coated hydroxyapatite plates
Abstract
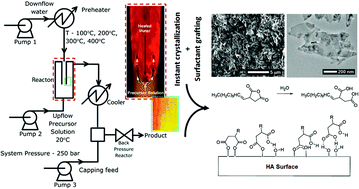
A continuous flow hydrothermal synthetic route which allows the direct “in situ” capping/coating of hydroxyapatite nanoplates with functional dispersants in a single stage is reported. The methodology induced crystallisation by rapid mixing of streams of preheated water and solutions of reagents in water, whilst the hydrophobic surface modification of the HA platelets was achieved without morphological disruption. The effect of adding the hydrocarbon either before or after the HA platelet formation point has also been assessed, proving that the presence of surfactant at the reaction site does not interfere with the formation of HA and allows for a more efficient binding and extraction of the inorganic materials. The coupling mechanisms between the surfactant and the HA surface have been proposed to be a mixture of covalent and electrostatic interactions (i.e. all forms of chemisorption). This synthesis route is fully scalable to pilot (10 tons per year) and industrial (1000 tons per year) scales.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...