Post-synthesis functionalization of a zeolitic imidazolate structure ZIF-90: a study on removal of Hg(ii) from water and epoxidation of alkenes
Abstract
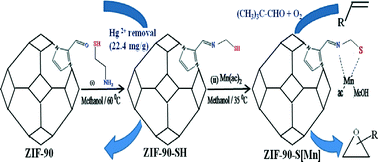
Thiol-functionalized ZIF-90 (ZIF-90-SH) was prepared via condensation of the free aldehyde group of ZIF-90 with 2-mercaptoethylamine to an imine through a one-step post-synthesis route. A subsequent reaction with manganese(II) acetate resulted in the formation of a new Mn(II)-immobilized hybrid material (ZIF-90-S[Mn]). This material was characterized by chemical analysis, X-ray diffraction, N2 adsorption–desorption, thermogravimetric analysis and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, which confirmed the successful functionalization of the as-synthesized ZIF-90. ZIF-90-SH employed as an adsorbent for the removal of Hg(II) ions from an aqueous solution at room temperature exhibited an adsorption capacity of ca. 22.4 mg g−1. The material showed 96–98% removal of Hg(II) ions in a low concentration range (0.1 to 10.0 mg L−1). ZIF-90-S[Mn] showed good catalytic activity and selectivity in the epoxidation of several important alkenes using molecular oxygen under atmospheric pressure. Recycling and hot filtration experiments coupled with a blank test showed that epoxidation proceeded over ZIF-90-S[Mn] on the external surface of the ZIF-90 matrices, where the active Mn(II) sites were located. The catalyst could be recycled up to four times without significant loss of efficiency.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...