((1H-tetrazol-5-yl) methyl) pyridine-based metal coordination complexes: in situ tetrazole synthesis, crystal structures, luminescence properties†
Abstract
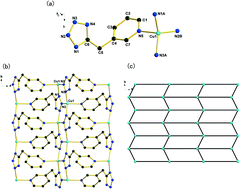
Six novel transition metal coordination complexes, [Cu(3TMP)] (1), [Zn(3TMP)Cl] (2), [Cd3(3TMP)4(N3)2]·0.38H2O (3), [Zn3(4TMP)2(OH)2(H2O)]·2(NO3) (4) and [M2(4TMP)(OH) (H2O)(SO4)] (M = Zn (5), M = Cd (6)) (3HTMP = 3-((1H-tetrazol-5-yl) methyl) pyridine; 4HTMP = 4-((1H-tetrazol-5-yl) methyl) pyridine), have been hydrothermally synthesized through in situ tetrazole synthesis. These complexes have been structurally characterized by single crystal and powder X-ray diffraction elemental analyses, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy as well as thermal studies. Complexes 1–6 are two or three-dimensional (3D) frameworks with structural diversity owing to the versatile coordination modes of the in situ generated flexible ligands. Complex 1 presents a reticular structure consisting of two-dimensional (2D) layers formed by the linkage between the pyridine rings and [Cu–tetrazole–Cu] wave-like chains. Complex 2 features a 3D framework built up by two kinds of helical chains composed of Zn(II) and the flexible ligand 3TMP. Complex 3 exhibits a 3D framework built up from 3TMP ligands and trinuclear [Cd3(N3)2] building units. Complex 4 crystallizes as a 3D coordination complex constructed from two-dimensional layers and the linkers of 4TMP ligands, with NO3− anions situated in the channels. Complexes 5 and 6 exhibit a 3D framework constructed from {M2(4TMP)(OH)}nn− (M = Zn (5), M = Cd (6)) layers and sulfate anions. In addition, the counterions, such as the Cl terminal ligand in 2, the N3 terminal ligand in 3, the μ2-OH bridging ligand in company with free NO3− anions in 4, and the μ3-OH bridging ligand in company with free SO42− anions in 5 and 6, have decisive influence on the dimensionality and functionality of the final complexes. Furthermore, the solid state luminescence properties of these complexes have been investigated.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...