Epitaxial growth of vertically aligned ZnO nanowires for bidirectional direct-current driven light-emitting diodes applications†
Abstract
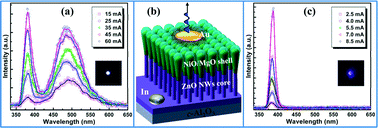
We presented a comparative investigation on the morphological and structural properties of the produced ZnO nanowires (NWs) on c-Al2O3 substrates under different preparation conditions. The effects of a low-temperature nucleation layer, reaction pressure and light irradiation on the alignment, diameter and growth rate of ZnO NWs were evaluated in detail. It was found that the low-temperature nucleation layer acting as a supporting layer favored the formation of a transition layer featuring initially a rough surface and a high density of grain boundaries, guiding and facilitating the subsequent homoepitaxy of ZnO NWs grown on the top of developed (0001) facets of the new activation sites. The crystallinity and vertical alignment of epitaxial ZnO NWs were further optimized to achieve the best value, as the second growth stage was conducted with a higher reaction pressure and light irradiation, such that a relatively low full width at half-maximum (701 arcsec) of the rocking curve could be obtained. The thermodynamical growth kinetics of the produced ZnO NWs via the two-step growth process was also investigated by monitoring the morphology evolution at different growth stages. Coaxial n-ZnO/MgO/p-NiO-core/shell NWs heterostructured light-emitting diodes (LEDs) were then fabricated and characterized, and a unique tunability of the electroluminescence (EL) spectra depending on the bias polarities was observed. We studied in detail the bicolor EL characteristic of the bidirectional direct-current driven LEDs and tentatively proposed carrier tunneling and hole generation models to explain such interesting features.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...