Fluorescent supramolecular polypseudorotaxane architectures with Ru(ii)/tri(bipyridine) centers as multifunctional DNA reagents†
Abstract
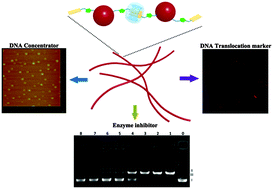
A water-soluble supramolecular polypseudorotaxane was prepared via the host–guest interaction of cucurbit[8]uril and the Ru(bpy)3 complex with bis-naphthalene groups. By employing the intrinsic properties of the Ru(bpy)3 complex, the linear polypseudorotaxane can induce DNA condensation, be used as an inhibitor for DNA cleavage enzymes, and trace the translocation of DNA into 293T cells efficiently.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...