DNA-functionalized Pt nanoparticles as catalysts for chemically powered micromotors: toward signal-on motion-based DNA biosensor†
Abstract
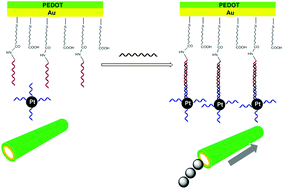
We present here the construction of a DNA biosensor based on a tubular micromotor that only produces motion-based signal in the presence of DNA target. This “turn on” characteristic of the sensor is achieved by the addition of Pt nanoparticle-DNA conjugate as the motion-inducing catalyst for the micromotors through DNA hybridization. Our work potentially offers new design strategies for motion-based biosensors with higher specificity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...