Following the aggregation of human prion protein on Au(111) surface in real-time†
Abstract
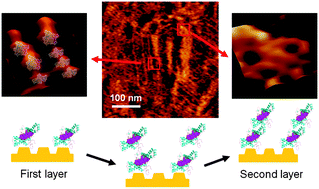
Aggregations of human prion protein (23–231) were monitored by atomic force microscopy in real-time under pH 4. Prion dimers and trimers were determined as the basic units by AFM images and simulated structures. Aggregates aligned with the herringbone structures of an Au(111) reconstructed surface via Au–S bonds as the first layer, while the second layer was formed by non-covalent interactions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...