Tuning the pore sizes of novel silica membranes for improved gas permeation properties via an in situ reaction between NH3 and Si–H groups†
Abstract
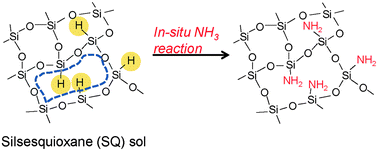
A new concept was proposed to control the pore size in a novel silica membrane. The tuning of the pore sizes in triethoxysilane (TRIES)-derived membranes was successfully conducted via an in situ reaction between NH3 and Si–H groups at high temperatures. The formation of Si–NH2 and/or Si–NH groups in the silica structure enhanced the hydrogen selectivity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...