Crystallization of hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles†
Abstract
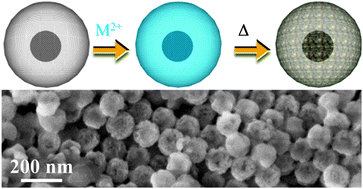
Complex 3D macrostructured nanoparticles are transformed from amorphous silica into pure polycrystalline α-quartz using catalytic quantities of alkaline earth metals as devitrifying agent. Walls as thin as 10 nm could be crystallized without losing the architecture of the particles. The roles of cation size and the mol% of the incorporated devitrifying agent in crystallization behavior are studied, with Mg2+, Ca2+, Sr2+ and Ba2+ all producing pure α-quartz under certain conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...