Determination of ultra-trace cobalt in water samples by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry after cloud point extraction using 2-(5-bromo-2-pyridylazo)-5-dimethylaminoaniline as the chelating agent
Abstract
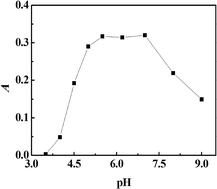
A new method for the determination of ultra-trace cobalt in water samples by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry after cloud point extraction using 2-(5-bromo-2-pyridylazo)-5-di methylaminoaniline (5-Br-PADMA) as the chelating agent and Triton X-114 as the extractant was established. The main parameters affecting extraction, such as pH, concentration, chelating agent, surfactant, equilibrium temperature and time, were investigated in detail. The optimized CPE conditions were as follows: pH = 5.5 HAc–NaAc buffer solution, 80 μL 5 × 10−4 mol L−1 5-Br-PADMA, 0.6 mL 1.0% (w/v) Triton X-114, and heat-assisted at 60 °C for 10 min. Under optimum conditions, the analytical curve was linear in the range of 0.05–1.0 ng mL−1 and the detection limit was 0.004 ng mL−1 for cobalt, the relative standard deviation was 3.3% (c = 0.5 ng mL−1, n = 6), and the recovery was 96.7–104.0%. The method was applied to the determination of ultra-trace cobalt in water with satisfactory results.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...