An experimental study on the evolution of aggregate structure in coals of different ranks by in situ X-ray diffractometry
Abstract
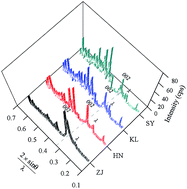
Coal samples of different ranks were selected based on geological ages and regions to investigate their thermal evolution in aggregate structure using in situ X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectroscopy. Samples were heated at a rate of 10 °C min−1 in the range of 25–900 °C. The XRD profiles of the coal samples displayed an evident decrease in intensity of peak at 20° (λ-band), which suggests the decomposition of oxygen-containing functional groups in the coal matrix at higher temperatures. In contrast, the peak at 26° (so-called G-band) became sharper and shifted to higher angles, which suggests a more ordered crystallite structure of coal with increasing heating temperature. Note that the integrally diffracted intensity of these two bands weakened intensely above 400 °C, which suggests that the coal aggregate structure may be loosened due to the depolymerization of the carbonaceous matrix in coal. The primary phase of weight loss for the low-rank coals took place in the range of 300–500 °C, but the high-rank coals had an obvious second pyrolysis reaction above 500 °C. Moreover, this study shows that the heating temperature effect plays a key role in the evolution of the interlayer spacing of the crystalline structure (d002) and height of the aromatic layers (Lc), whereas the diameter of the aromatic layers (La) is more dependent on coal ranks rather than heating temperature.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...