Cyclic voltammetric determination of glutamic-pyruvic transaminase activity based on transdeamination
Abstract
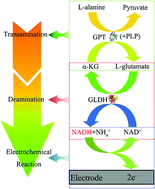
Glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (GPT) is one of the most important enzymes in human liver and has a valuable clinical reference for the diagnosis of many liver diseases. Here a method for the determination of GPT activity based on transdeamination is presented. In this method, a three electrode setup was used for the cyclic voltammetric determination of the enzyme. With the electrochemical detection of reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) produced from transdeamination, the GPT activity was characterized under optimal circumstances. Firstly, to verify the response of the electrode to NADH, a series of NADH concentrations varying from 39 μM to 2.5 mM were calibrated with cyclic voltammetry (CV). A linear relationship between the NADH concentration and the peak current with R2 0.9999 was obtained. Then the concentration of α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) which can exert great influence on transdeamination was also optimized and the most sensitive response was achieved at the point of 0.75 mM α-KG. Finally, the GPT activity was determined using both the unmodified screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE) and the electrode modified with CNTs. The results showed that the relationship between the GPT activity and the peak current of the CV curve was linear between 60 U L−1 and 300 U L−1 and the modified electrode exhibited a slightly better linear relationship than the unmodified electrode. This work proposes a new enzymatic reactive system based on transdeamination for the electrochemical detection of GPT activity and combines the electrochemical detection of NADH with the determination of GPT activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...