Concentration addition prediction for a multiple-component mixture containing no effect chemicals†
Abstract
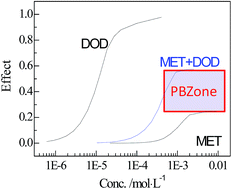
The concentration addition (CA) model is usually used to assess toxicological interaction and predict mixture toxicity. However, when the maximum effect of a mixture is different from that of a single component, it is impossible to directly use CA to predict the mixture concentration (cmix) at some effect zones that are called predictive blind zones (PBZones). A mixture containing no effect chemicals (NECs) is a special case of the PBZone. Aiming at this special PBZone, we assumed the ECx of NECs to be infinity at all effects and thus readily computed various cmixs in PBZones. At the same time, the combination index (CIx) combined with its 95% observation-based confidence intervals (OCIx) was employed to characterize the toxicological interaction. The approach was successfully used to predict the combined toxicity and assess the toxicological interactions of five chemicals, imidacloprid and metalaxyl (pesticides), 1-butylpyridinium bromide (ionic liquid), and apramycin sulfate and neomycin sulphate (antibiotics, being NECs). The results showed that except for the toxicological interactions of five mixture rays at higher effects than 25% being antagonistic, all the other mixtures are due to additive action.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...