Targeted quantitative analysis of anthraquinone derivatives by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry to discriminate between crude and processed rhubarb samples†
Abstract
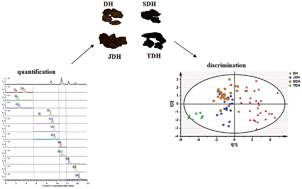
Crude rhubarb has been used as a drastic laxative for thousands of years in China. To alleviate celialgia and moderate drastic effects, crude rhubarb is subjected to processing prior to clinical use. In the present study, a targeted plant metabolomic method using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in segmental multiple reaction monitoring mode was developed to simultaneously determine 13 marker constituents (two anthrones, six anthraquinone glycosides and five anthraquinone aglycones) in rhubarb. With satisfactory linearity, precision and accuracy, the developed method was then applied to explore the content variations of these compounds in crude and processed rhubarbs. After processing, the total content of anthraquinone glycosides decreased significantly, which might result in a mild purgative function. Moreover, based on the contents of the marker compounds, unsupervised principal component analysis was employed to differentiate samples of 81 batches covering both crude and processed rhubarbs. The results indicated that the targeted quantification of marker compounds by LC-MS/MS coupled with PCA would be a reliable strategy to discriminate crude and processed herbs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...