Single-walled carbon nanotubes–carboxyl-functionalized graphene oxide-based electrochemical DNA biosensor for thermolabile hemolysin gene detection
Abstract
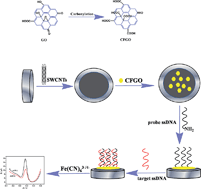
A sensitive electrochemical DNA biosensor, based on carboxyl-functionalized graphene oxide (CFGO), a single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) sensing platform and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) detection, was constructed in this study. CFGO was prepared via a ring-opening reaction catalyzed by hydrobromic acid and an esterification reaction with oxalic acid, and used as a mediator for probe DNA (pDNA) immobilization. DNA labeled at 5′-end using amino (NH2-pDNA) was immobilized on the electrode surface through covalent interaction between amino and carboxyl groups on CFGO. Moreover, single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) were employed to improve the electrochemical performance of the biosensor. Based on the different electrochemical responses of [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− toward pDNA versus double-stranded DNA after hybridization, the thermolabile hemolysin gene sequence could be detected in a concentration range from 1 × 10−6 to 1 × 10−13 mol L−1 with a low detection limit of 7.21 × 10−14 mol L−1 (at a signal-to-noise ratio of 3). Furthermore, the biosensor also displayed high selectivity for the differentiation of DNA oligonucleotides from one-base mismatch to noncomplementary. All the reasonable electrochemical performance of the proposed sensing platform indicated that it could be used for the sensitive and accurate determination of other nucleic acids.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...