Quantification of phenol in urine headspace using SIFT-MS and investigation of variability with respect to urinary concentration
Abstract
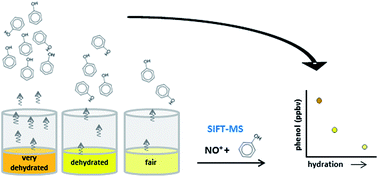
To quantify phenol in human urine or exhaled breath using selected ion flow tube mass spectrometry (SIFT-MS) requires a careful study of its reactions with the appropriate SIFT-MS precursor ions in the presence of water vapour. The reactions of NO+ precursor ions with the isobaric compounds phenol and dimethyl disulphide (DMDS) have been studied using the SIFT technique to identify the appropriate product ions in order to optimise the SIFT-MS kinetics library entries for these compounds. This allows accurate quantification when these compounds co-exist in humid biofluids, in particular urine headspace and exhaled breath. These optimised kinetics library entries have been used to investigate the effect of hydration status of healthy individuals on the concentration of phenol in their urine. Using these new kinetics, it is seen that hydration status of the donor volunteers (assessed using urinary osmolality and creatinine concentration) affects urinary headspace phenol concentrations measured via SIFT-MS. A strong correlation between headspace phenol concentration and both the urinary osmolality and urinary creatinine concentration has been demonstrated. Thus, to obtain urinary concentrations of phenol by headspace analyses using SIFT-MS it is essential to account for the osmolality or creatinine concentration of the urine.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...