Determination of cadmium, cobalt, copper, lead, nickel and zinc contents in saline produced water from the petroleum industry by ICP OES after cloud point extraction
Abstract
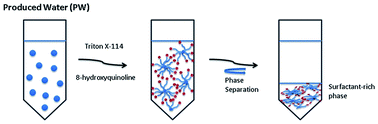
The aim of this study was to develop a cloud point extraction (CPE) method to determine simultaneously cadmium, cobalt, copper, nickel, lead and zinc contents in produced water by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP OES). A full factorial design with a central point was applied for optimization of experimental conditions. 8-Hydroxyquinoline was used as the chelating agent and Triton X-114 as the surfactant for trace element extraction. ICP OES with an axial view configuration was used in the trace element determination. According to the desirability function, the chelating agent showed a negative influence on the extraction of the studied elements, which means increasing the amount of non-ionic molecules of the chelating agent may cause the opposite effect, since these molecules may be captured by the micelles decreasing the efficiency of extraction. In contrast, the extraction was positively influenced by the surfactant. Therefore, the following parameters were chosen: pH = 6.5; 0.500 mmol L−1 8-hydroxyquinoline; and 0.1% v/v Triton X-114. The influence of salinity on the CPE was investigated. The slopes of the analytical calibration curves in saline media were studied. It was observed that increasing the NaCl concentration from 5 to 50% (w/v) led to a decrease in the angular coefficient of the calibration curves, which implies a decrease in the sensitivity of the method. Sc (2 mg L−1) was added to standards and samples as the internal standard to correct non-spectral interference. The accuracy of the developed method was confirmed by spike recovery tests. The results present good recoveries, exceeding 86%, showing the successful application of the method for the simultaneous determination of Cd, Co, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn contents in produced water samples. Limits of quantification (LOQ) were determined to be 2.0, 2.2, 3.2, 0.23, 2.2 and 1.9 μg L−1 for Cd, Co, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn, respectively.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...