Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for chenodeoxycholic acid using an anti-chenodeoxycholic acid monoclonal antibody
Abstract
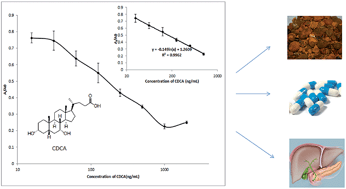
CDCA is one of the major bile acids in humans and has important clinical significance and therapeutic applications. In this work, a new monoclonal antibody (MAb) specific for chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) was prepared and characterized. A hybridoma secreting an anti-CDCA MAb was produced by fusing splenocytes from a mouse immunized against a CDCA–BSA conjugate with the hypoxanthine–aminopterin–thymidine (HAT)-sensitive mouse myeloma cell line Sp2/0-Ag14. The antibody was highly specific for CDCA, exhibited only weak reactions with CA and DCA and did not react with other structurally related chemicals. Subsequently, a MAb-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) against CDCA was developed and characterized. In this assay, we detected an effective CDCA measurement range of 32 ng mL−1 to 1024 ng mL−1 (R2 = 0.9962). Both intra-assay and inter-assay repeatability and precision were achieved with relative standard deviations (RSD) below 10%. Additionally, the CDCA levels in medicines and samples were determined with high sensitivity and efficiency. This study provides a useful method for detecting CDCA in medicines and will contribute to the further clinical research.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...