Sensitive determination of two major mercapturic acid metabolites of 1,3-butadiene in human urine based on the isotope dilution ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry†
Abstract
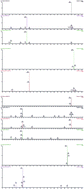
1,3-Butadiene is widely used as a chemical intermediate to produce chemicals and is a worldwide environmental pollutant. The major urinary metabolites of 1,3-butadiene are 3,4-dihydroxybutyl mercapturic acid (DHBMA) and monohydroxy-3-butenyl mercapturic acid (MHBMA), which are usually used as biomarkers for exposure to this carcinogenic substance. Here, we developed and validated a selective and sensitive method for the quantitative determination of DHBMA and MHBMA in human urine. Firstly, two mercapturic acids were extracted from urine samples using solid phase extraction. Then, they were separated with an Acquity BEH C18 column using gradient elution. Finally, the analytes were identified and quantified based on isotope dilution ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Under the optimal conditions, the recovery rates ranged from 87.1% to 107.9% with a coefficient of variation ≤14.8%. The limits of detection were 0.14 and 0.16 ng mL−1 for DHBMA and MHBMA, respectively. Owing to the good accuracy, precision and high sensitivity, the proposed method is well suitable for application in simultaneous determination of mercapturic acids in human urine.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...