Rapid assay for testing superoxide anion radical scavenging activities to natural pigments by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-diode-array detection method
Abstract
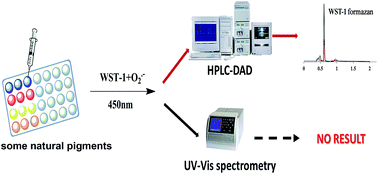
As a result of the donation of one electron, superoxide anion radicals (O2˙−) are produced in vivo, which are closely linked with several diseases in humans. In the past decades, some analytical methods for the determination of O2˙− scavenging capacity have been established. The most common methods in vitro are spectrum-based microplate screening assay using nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) or cytochrome c as the target/probe for evaluating O2˙− scavenging activity. The target/probe is spectrophotometrically monitored at the ultraviolet-vis (UV-vis) region in the analysis of the samples with restraining UV-vis absorption. Nevertheless, the results of these methods were severely compromised when they were applied to analyze the samples with strong absorption in the visible region, such as natural pigments. To solve these problems, a simple and rapid assay combined with a new probe, a highly water-soluble tetrazolium salt, 2-(4-iodophenyl)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-(2,4-disulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium sodium salt (WST-1) and ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-diode-array detection (UPLC-DAD) method was developed. Above all, this method could be adapted to samples of strong absorption in the visible region. In this study, the superoxide anion radical scavenging activities of various natural pigments were evaluated.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...