A correlation model of UPLC fingerprints and anticoagulant activity for quality assessment of Panax notoginseng by hierarchical clustering analysis and multiple linear regression analysis†
Abstract
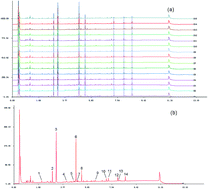
Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F.H. Chen (commonly known as Tianqi or Sanqi) is a famous traditional Chinese medicine and has been widely used in the treatment of cardio- and cerebro-vascular diseases. However, the quality assessment of Sanqi is quite difficult because of the ingredient complexity. In this work, the chemical fingerprints of 15 batches of P. notoginseng from different sources were investigated by ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC). Fourteen common peaks in these samples were detected including 20(S)-protopanaxatriol saponins (PTS) and 20(S)-protopanaxadiol saponins (PDS). These samples were divided into three clusters by hierarchical clustering analysis (HCA). Clusters I and III possessed stronger anti-coagulation effects than Cluster II. Multiple linear regression analysis (MLRA) showed that notoginsenoside R1, ginsenoside Rb1, ginsenoside Rd and an unknown compound might be the major effective compounds for the quality control of Sanqi. PDS (Rb1, Rd, and the unknown compound) possesses a stronger anticoagulant activity than PTS (R1 only). This conjecture was confirmed by the dose–effect relationship evaluation of PDS and PTS. This study provides a general correlation model of the fingerprint and efficacy relationship for the quality control of Sanqi and other TCMs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...