Monodispersity of magnetic immuno-nanoprobes enhances the detection sensitivity of low abundance biomarkers in one drop of serum†
Abstract
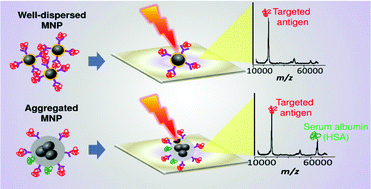
To enhance the detection sensitivity of target clinical protein biomarkers, a simple and rapid nanoprobe-based immuno-affinity mass spectrometry assay employing biocompatible monodisperse magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) is reported herein. The MNPs were synthesized via a streamlined protocol that includes (a) fabrication of core MNPs using the thermal decomposition method to minimize aggregation, (b) surface protection by gold coating (MNP@Au) and surfactant coating using MNP@IGEPAL to improve hydrophilicity, and lastly, (c) oriented functionalization of antibodies to maximize immuno-affinity. The enrichment performances of the monodisperse MNPs for the C-reactive protein (CRP) serum biomarker were then evaluated and compared with aggregated magnetic nanoparticles synthesized from the conventional co-precipitation method (MNPCP). The detection sensitivity for CRP at an extremely low amount of serum sample (1 μL) was enhanced ∼19- and ∼15-fold when monodisperse MNP@Au and MNP@IGEPAL, respectively, were used. Furthermore, the detection sensitivity of CRP by this approach (1 ng mL−1, S/N = 3) provided a 1000-fold sensitivity enhancement to the clinical cut-off (1 μg mL−1) of CRP. We supposed that these observed improvements are due to the enhanced nanoparticle dispersibility and size uniformity which eliminated completely other non-specific binding of high-abundance serum proteins. Most interestingly, the enrichment efficiency correlates more closely with the MNP dispersibility than the ligand density. Our investigation revealed the critical role of MNP dispersibility, as well as provided mechanistic insight into its impact on immunoaffinity enrichment and detection of CRP in one drop of serum sample. This strategy offers an essential advantage over the other methods by providing a simple and facile biofunctionalization protocol while maintaining excellent solvent dispersibility of MNPs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...