Voltage and blockade state optimization of cluster-enhanced nanopore spectrometry
Abstract
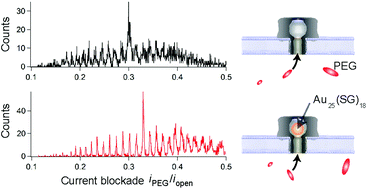
Recent work described the use of thiolate-capped gold clusters (Au25(SG)18) with nanopore sensing to increase the residence time of polyethylene glycol (PEG) in an alpha hemolysin pore [Anal. Chem., 2014, 86, 11077]. It was shown that the residence time enhancement narrows the peaks in the PEG-induced current blockade distribution, thus increasing the resolving power of the single molecule nanopore spectrometry (SMNS) technique. Here, we further study the interaction between the cluster and PEG with the goal of optimizing the residence time enhancement for SMNS detection. Specifically, we report the voltage dependence of the enhancement effect and show that, under the conditions studied, the cluster-enhanced residence time is maximized at an applied transmembrane potential near 60 mV. Additionally, we show that the PEG residence time depends on the degree to which the cluster blocks current through the pore and that the PEG on-rate to the pore can be more accurately measured with a cluster in the pore. Finally, we develop a model that describes the cluster-induced shift of the PEG current blockade distribution. We use this model to characterize the interaction between the cluster and PEG and show that it scales linearly with the applied voltage as expected from the proposed enhancement mechanism.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...