Strand displacement activated peroxidase activity of hemin for fluorescent DNA sensing†
Abstract
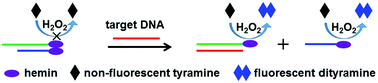
To efficiently regulate the catalytic activity of the peroxidase mimic hemin, this work designs a double-stranded DNA probe containing an intermolecular dimer of hemin, whose peroxidase activity can be activated by a DNA strand displacement reaction. The double-stranded probe is prepared by annealing two strands of hemin labelled DNA oligonucleotides. Using the fluorescent oxidation product of tyramine by H2O2 as a tracing molecule, the low peroxidase activity of the hemin dimer ensures a low fluorescence background. The strand displacement reaction of the target DNA dissociates the hemin dimer and thus significantly increases the catalytic activity of hemin to produce a large amount of dityramine for fluorescence signal readout. Based on the strand displacement regulated peroxidase activity, a simple and sensitive homogeneous fluorescent DNA sensing method is proposed. The detection can conveniently be carried out in a 96-well plate within 20 min with a detection limit of 0.18 nM. This method shows high specificity, which can effectively distinguish single-base mismatched DNA from perfectly matched target DNA. The DNA strand displacement regulated catalytic activity of hemin has promising application in the determination of various DNA analytes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...