Restricted accessed nanoparticles for direct magnetic solid phase extraction of trace metal ions from human fluids followed by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry detection†
Abstract
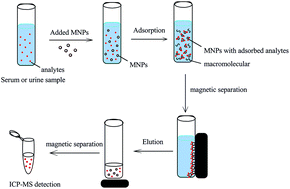
Herein, restricted accessed magnetic nanoparticles were synthesized by self-assembly of a non-ionic surfactant (Tween-20) onto the 4-(2-pyridylazo)resorcinol (PAR) functionalized magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs). A series of analytical techniques were employed for the characterization of the as-prepared restricted accessed Fe3O4@SiO2@PAR, and it was found that the as-prepared restricted accessed Fe3O4@SiO2@PAR nanoparticles have a porous structure with a BET surface area of around 99.4 m2 g−1, an average pore size of about 6.14 nm and a pore volume of 0.47 cm3 g−1. Besides, the prepared restricted accessed Fe3O4@SiO2@PAR showed good size exclusion properties toward proteins, providing application potential for the direct analysis of biological samples. Based on this, a novel method of restricted accessed magnetic solid phase extraction (MSPE) combined with inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) was developed for the direct determination of trace metal ions in human fluids. The parameters affecting the extraction of the target metals by MSPE were studied and the optimized conditions were established. Under the optimum conditions, the adsorption capacity of Cr(III), Cd(II), La(III), Nd(III) and Pb(II) on the as-prepared restricted accessed Fe3O4@SiO2@PAR was 62.9, 56.6, 33.7, 36.9 and 43.3 mg g−1, respectively. With an enrichment factor of 30, the limits of detection for Cr(III), Cd(II), La(III), Nd(III) and Pb(II) were as low as 11.9, 0.8, 0.7, 1.6 and 4.1 ng L−1, and the relative standard deviations were 7.6, 8.7, 8.4, 8.1 and 5.0 (CCr, Pb = 0.05 μg L−1, CCd, La = 0.005 μg L−1, CNd = 0.01 μg L−1, n = 7), respectively. The developed method was successfully applied for the direct analysis of free metal ions in human urine and serum samples, and has the advantages of good anti-interference ability, high sensitivity and exhibits great application potential in the direct analysis of trace metals in biological fluids.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...