Surface invasive cleavage assay on a maskless light-directed diamond DNA microarray for genome-wide human SNP mapping†
Abstract
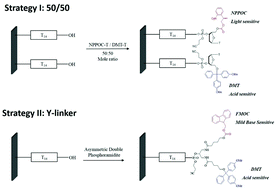
The surface invasive cleavage assay, because of its innate accuracy and ability for self-signal amplification, provides a potential route for the mapping of hundreds of thousands of human SNP sites. However, its performance on a high density DNA array has not yet been established, due to the unusual “hairpin” probe design on the microarray and the lack of chemical stability of commercially available substrates. Here we present an applicable method to implement a nanocrystalline diamond thin film as an alternative substrate for fabricating an addressable DNA array using maskless light-directed photochemistry, producing the most chemically stable and biocompatible system for genetic analysis and enzymatic reactions. The surface invasive cleavage reaction, followed by degenerated primer ligation and post-rolling circle amplification is consecutively performed on the addressable diamond DNA array, accurately mapping SNP sites from PCR-amplified human genomic target DNA. Furthermore, a specially-designed DNA array containing dual probes in the same pixel is fabricated by following a reverse light-directed DNA synthesis protocol. This essentially enables us to decipher thousands of SNP alleles in a single-pot reaction by the simple addition of enzyme, target and reaction buffers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...