A rapid response “Turn-On” fluorescent probe for nitroreductase detection and its application in hypoxic tumor cell imaging†
Abstract
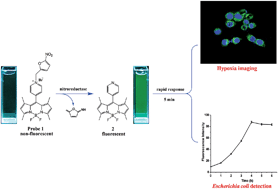
A novel “Turn-On” fluorescent probe, quaternarized 4-pyridinyl-substituted BODIPY dye by incorporating a 5-nitrofuran moiety, was developed and applied for imaging the hypoxic status of tumor cells by the indirect detection of nitroreductase. The design was based on a nitroreductase-catalyzed reduction of the nitrofuran moiety in the presence of reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) as an electron donor and followed by the 1,6-rearrangement-elimination and the release of free 4-pyridinyl-substituted BODIPY dye 2. This probe displayed desired properties such as high specificity, “Turn-On” fluorescence response with suitable sensitivity, appreciable water solubility and rapid response time (within 5 min). Moreover, as a biocompatible molecule, the probe has been successfully applied for imaging the hypoxic status of tumor cells (e.g. A549 cells) and especially used for real-time determination of nitroreductase produced by Escherichia coli. Therefore, we hope to apply this novel method in the biomedical research fields for the imaging of disease-relevant hypoxia and detection of pathogenic microorganisms.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...