Engineered-membranes and engineered-micelles as efficient tools for purification of halorhodopsin and bacteriorhodopsin
Abstract
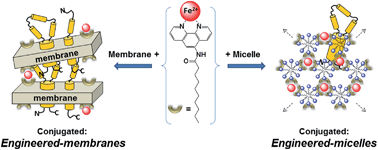
We describe two alternative and complementary purification methods for halorhodopsin and bacteriorhodopsin. The first relies on a unique form of detergent micelles which we have called engineered-micelles. These are specifically conjugated in the presence of [hydrophobic chelator:Fe2+] complexes and form detergent aggregates into which membrane proteins partition, but hydrophilic water-soluble proteins do not. The approach was tested on the membrane protein, bacteriorhodopsin (bR), with five non-ionic detergents (OG, OTG, NG, DM, and DDM), commonly used in purification and crystallization of membrane proteins, in combination with the commercially available bathophenanthroline or with one of the three synthesized phenanthroline derivatives (Phen-C10, Phen-C8 and Phen-C6). Our results show that bR is extracted efficiently (60–86%) and directly from its native membrane into diverse detergent aggregates with preservation of its native conformation, while 90–95% of an artificial contaminating background is excluded. For implementation of the second method, based on engineered-membranes, the use of detergents, which in some cases may produce protein denaturation, is not required at all. Protein-containing membranes are conjugated via the same hydrophobic [chelator:metal ion] complexes but maintain the membrane protein in its native bilayer environment throughout the process. This method is demonstrated on the membrane protein halorhodopsin from Natronomonas pharaonis (phR) and leads to good recovery yields (74–89%) and removal of >85% of artificial background impurities while preserving the native state of phR. The detailed structure of the hydrophobic chelator used has been found to have a marked effect on the purity and yield of both methods.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...