A resonance energy transfer approach for the selective detection of aromatic amino acids†
Abstract
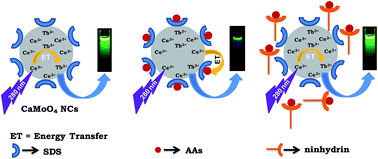
In this article, we report for the first time the use of Ln3+-doped nanocrystals to detect aromatic amino acids (AAs) up to nanomolar concentration. Detection of AAs is important for several reasons. For instance, increased levels of AAs are detected in the early phase of gastric carcinogenesis in gastric juice samples. In this work, we have shown that the highly efficient energy transfer between Ce3+ and Tb3+ ions in Ce3+/Tb3+-doped CaMoO4 nanocrystals is selectively altered by the addition of AAs, thus providing a simple resonance energy transfer (RET) approach to detect AAs in the nanomolar (nM) range. This is achieved as the absorption spectrum of AAs overlaps with the emission spectrum of the Ce3+/Tb3+-doped CaMoO4 nanocrystals, thus reducing the energy transfer efficiency between the Ce3+ and Tb3+ ions. This selective energy transfer process leads to the quenching of the Tb3+ emission from the nanocrystals. The high selectivity was verified by the addition of essential or non-essential amino acids, and some metal ions and molecules that generally coexist with AAs in our body. Moreover, the selective quenching of the Tb3+ ion emission can be easily reversed by the addition of ninhydrin; 90% of the initial luminescence intensity is recovered during the reversal process. This process was repeated for more than five cycles with only a slight decrease in the sensing ability. The study was also extended to 2D surfaces where the nanocrystals are strongly attached to a positively charged surface, which, upon dipping into the AA solution, leads to the quenching of the luminescence exhibited by the Tb3+ ions. The signal can be easily recovered after ninhydrin treatment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...