Electronic transition responsible for size-dependent photoluminescence of colloidal CuInS2 quantum dots
Abstract
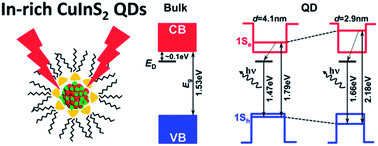
Colloidal CuInS2 quantum dots with an average size of 2.9–4.1 nm were synthesized by the one-pot heating of an organometallic solution. The size-dependent optical gaps and photoluminescence (PL) emission energies were analyzed based on the finite-depth well effective mass approximation. The PL emission was attributed to the recombination of electrons in the donor level and holes in the quantized hole state. Indium atom defects at copper sites or sulfur vacancies were proposed to be the defects acting as donors at ∼0.1 eV below the conduction band.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2014 Journal of Materials Chemistry C Hot Articles

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...