Soft- and hard-templated organic salt nanoparticles with the Midas touch: gold-shelled nanoGUMBOS
Abstract
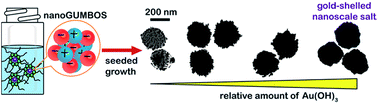
An emerging thrust in the design of advanced materials is nanoscale functional materials possessing multiple capabilities, such as those possessing a core–shell architecture. Nanoparticles comprising a dielectric core (e.g., silica, polystyrene) and a gold shell are particularly attractive due to the desirable optical (plasmonic) and biocompatibility characteristics of gold. While these materials are bio-inert, they generally present limited tunability. In this regard, a core composed of a solid-state ionic liquid represents an interesting and unexplored alternative for generating unique core–shell architectures. In recent years, we have developed an emergent class of morphology-controlled tailored organic salt particles, so-called GUMBOS (group of materials based on organic salts). GUMBOS are reminiscent of traditional ionic liquids with the important distinction that they possess elevated melting points (generally, from 100 to 250 °C), making possible the fabrication of ambient-stable nanoscale salts of various sizes, compositions, and morphologies by means of a variety of thermal, sonochemical, colloidal, or hard-template synthetic routes. In this work, we advance our recent examination of GUMBOS to demonstrate proof of concept for their use in elaborating novel plasmonic nanostructures by using a seed-mediated growth to generate gold shells atop nanoscale quasi-spherical GUMBOS as well as uni-dimensional GUMBOS nanorods. We present here our general strategy for preparing gold-shelled nanoGUMBOS, alongside systematic monitoring of the evolution of the gold-coating process. We also report on a preliminary investigation of the catalytic properties of the near-infrared absorbing gold-shelled nanorod GUMBOS in the reduction of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol using sodium borohydride.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...