Effect of head group size on the photoswitching applications of azobenzene Disperse Red 1 analogues†
Abstract
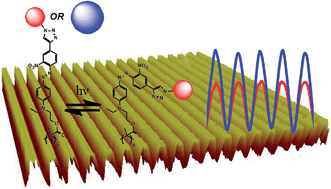
We investigate the effect of the increased molecular bulk in the ‘head’ group for a class of newly synthesized azobenzene chromophores with a clickable ethynyl group para and a nitro group ortho to the azo bond on the distal benzene ring. This ‘variable-head’ functionalization provides a family of dyes with photophysical characteristics very similar to those of Disperse Red 1, one of the most commonly used azo dyes in materials science. Phenyl, naphthyl, and anthracyl derivatives were synthesized as small molecules, monomers, homopolymers, and copolymers in a rapid and facile manner using click chemistry, confirming the versatility of this parent chromophore. Photochemical and spectral studies indicate that this strategy is suitable to build a ‘bulkiness series’ of stimuli-responsive materials, as the various material derivatives retain the absorption and kinetic characteristics of the parent chromophore necessary for all optical patterning applications that DR1 dyes have been optimized for. In thin films, larger head group size was found to increase the stability of light-induced birefringence in copolymers. The homopolymers formed stable surface-relief gratings upon interference irradiation, whose grating depths correlate with head group size, demonstrating that this new class of polymers can also undergo tailored macroscopic photoinduced motions, which could have applications in all optical nano-patterning.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2014 Journal of Materials Chemistry C Hot Articles

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...