Surface modification of polymers by reduction of diazonium salts: polymethylmethacrylate as an example
Abstract
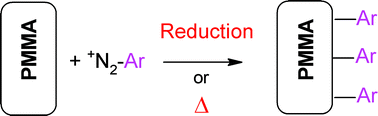
This paper describes the grafting of diazonium salts on polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA), a polymer of wide use. Diazonium salts have been grafted by reduction with hypophosphorous acid, or by thermal decomposition. The nanometer thick films have been characterized by IR, XPS and water contact angle and the thickness of the film estimated. With long chain perfluoroalkyl substitutents on the aryldiazonium group a water contact angle of 108° can be obtained on the smooth polymer, highlighting a hydrophobic surface. This process could be useful for modifying the PMMA surface when used as a glass substitute or as a substrate for microfluidic devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...