One pot synthesis of monodisperse water soluble iron oxide nanocrystals with high values of the specific absorption rate†
Abstract
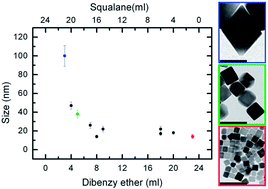
We report a highly reproducible route to synthesize iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) with control over size and shape and with size dispersions around 10%. By tuning the relative ratio of squalane to dibenzyl ether, which were used as solvents in the synthesis, the size of the particles could be varied from 14 to around 100 nm, while their shape evolved from cubic (for size ranges up to 35 nm) to truncated octahedra and octahedra (for sizes from 40 nm up to 100 nm). Fine tuning of the size within each of these ranges could be achieved by varying the heating ramp and the iron precursor to decanoic acid ratio. We also demonstrate direct water transfer of the as-synthesized IONPs via in situ ligand exchange with gallol polyethylene glycol molecules, the latter simply added to the crude nanocrystal mixture at 70 °C. The specific absorption rate (SAR) values measured on the water transferred IONPs, at frequencies and applied magnetic fields that are considered safe for patients, confirmed their high heating performance. Finally, this method allows the transfer of 35 nm nanocubes as individually coated and stable particles to the water phase. For the first time, the heating performance of such large IONPs has been studied. This work uncovers the possibility of using large IONPs for magnetic hyperthermia in tumor therapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...